Team:Tyngsboro MA Tigers
From 2012hs.igem.org
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
|[[REFERENCES]] | |[[REFERENCES]] | ||
| | | | ||
| - | |['''FUN'''DRAISING]] | + | |[['''[[FUN]]'''DRAISING]] |
|} | |} | ||
<!--- Team Information Link ---> | <!--- Team Information Link ---> | ||
Revision as of 19:34, 12 April 2012
| OUR PROJECT | TEAM | NOTEBOOK | CREATING THE GENETIC CIRCUIT | SAFETY | ATTRIBUTIONS | HUMAN PRACTICES | FUN FACTS | REFERENCES | [[FUNDRAISING]] |
Contents
|
Team
We're the eleven-strong inaugural Tiger Squad at Tyngsborough High School in Tyngsborough, Massachusetts, with a real interest in using our science knowledge to help the community and learn about synthetic biology along the way!
Instructors File:.jpg Rebekah Ravgiala
'TEAM MEMBERS
 Kathleen Barrett (Liaison)
Kathleen Barrett (Liaison)
Mia Pavao (Secretary)
 Lizzy Seltz (Lab Manager)
Lizzy Seltz (Lab Manager)

 Elizabeth Barrett (Public Relations)
Elizabeth Barrett (Public Relations)
 Madison Vigneault (co-Treasurer)
Madison Vigneault (co-Treasurer)
 Taylor Vigneault (co-Treasurer)
Taylor Vigneault (co-Treasurer)
 Brian Fidler (Morale Booster)
Brian Fidler (Morale Booster)
 Kevin Barrett (Programmer)
Kevin Barrett (Programmer)
 Shannon Jackson (Business Coordinator)
Shannon Jackson (Business Coordinator)
 Brian Parlee (Tech Support)
Brian Parlee (Tech Support)
Project Description
eCOlfactory: An olfactory test for the detection of carbon monoxide
According to the National Conference of State Legislatures [1], 25 states have statutes requiring residential carbon monoxide detectors. Currently, the common household CO detectors sold on the market are only sound-based. However, as people age, their senses become less acute. We are investigating the development of a genetic circuit for an indole-free E. coli chassis that converts the odorless carbon monoxide into an indole output - the naturally produced smell of bacteria. Coupled with the common household detector, we might be able to greatly reduce the number of CO-related deaths. Our cell could help save even more lives with another sensory warning of the hidden danger.
A colorless, odorless, and soundless killer takes the lives of nearly 2,100 unsuspecting United States citizens every year; that translates to an average of three people every day. Carbon monoxide poisoning is the leading cause of unintentional poisoning deaths in the United States, and one in every 2,400 people falls victim to CO poisoning, unaware of the invisible attacker. People over the age of 65 have the highest risk of falling victim to this silent killer [2]. Only by being aware of the grave danger, and understanding the structure and function of this gas, we can create a circuit that produces a scent to CO and a warning before it's too late.
The mechanism for CO detection in our system is derived from the bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum that naturally metabolizes CO as an energy source. This photosynthetic bacterium accomplishes this task in the following chemical reaction: CO + H2O --> CO2 + H2
The enzyme carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (CODH) is a peripheral membrane protein that carries out the primary oxidation of CO to CO2 and then passes the products through a ferredoxin-like sub-unit. R. rubrum also has a carbon monoxide-sensing protein called CooA that activates the gene expression of oxidation enzymes. In our research of R. rubrum, we found that a Turkey iGEM team in the 2010 college division developed CooA and CooA-responsive promoter BioBricks they wanted to make to transform into E. coli. They were able to successfully build these parts, and now our goal is to try and put them into our own genetic circuit that, in the presence of carbon monoxide, will output an unpleasant warning smell.
NOTEBOOK
Finding Our Idea
Our Team meets every Thursday from 2-4pm. Below you will find summaries of our meetings, as well as links to the agenda lists.
10/4/11-
10/11/11 -
10/18/11-
10/25/11-
11/3/11-
11/17/11-
12/1/11-
12/8/11-
12/15/11-
12/23/11-
1/5/12-
1/12/12-
1/19/12-
1/26/12-
2/2/12-
2/9/12-
2/16/12-
2/23/12-
3/1/12-
3/8/12-
3/15/12- Our project description was the focus of our meeting... What should be our project title? --should we be boring and say what it does-- what about "An olfactory system for the detection of carbon monoxide"-- should it start with " E. COLi factory:"-- Our final choice is.... "E. COLfactory: A smell test for the detection of carbon monoxide."
3/22/12- As Spring sports begin, we are experiencing a decline in team member attendance to our meetings. Should we consider supplementing our after school meetings with early morning as well? On a high note... we received a generous donation in the amount of $150 from Granite Ridge Energy to help supplement our fundraising efforts! Thank you for your contribution!!!!
3/29/12- We are trying to find a way to safely produce a controlled amount of CO in a lab. We found an experiment online that produced CO using sulfuric acid and formic acid ( H2SO4(l) + HCOOH(l) CO(g) + H2SO4.H2O(l) ) the lab procedure is found here: http://mattson.creighton.edu/CO/index.html
4/5/12-
4/12/12-
4/19/12- APRIL Vacation
4/26/12-
5/3/12-
5/10/12-
5/17/12-
5/24/12-
5/31/12-
6/7/12-
6/14/12-
6/21/12-
6/28/12-
Creating the Genetic Circuit
Once we had our idea solidified, the next step was coming up with a circuit to make our idea into a reality. Using the [http://www.tinkercell.com/ TinkerCell] program to create an example of the cell, we wanted to follow the KISS rule and keep things as simple as possible. The 2010 METU iGEM team created a [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K352014 part] that successfully detected carbon monoxide, and contained a Lacl promoter, RBS, and CooA, but from that point what the output was seemed to be fairly open for change. We wanted the output smell to be very unpleasant and trigger a negative response, and decided indole, the smell naturally made by e. coli, would be an excellent choice. We chose tnaA, the indole producing gene, as the last major step in our genetic sequence, and an [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_J45999 odorless chassis] so that indole wouldn't be naturally produced by the detector.
Obstacles in creating the circuit were finding a tnaA producing gene (still working on that) and...
The parts chosen were all marked as 'working' in the parts registry, and most had the same assembly methods, making them compatible. Our major concerns are that we won't be able to find a tnaA gene by itself, or that the parts chosen won't work be compatible in practice.
Also, special thanks go out to our iGEM advisers, Alyssa Henning, !
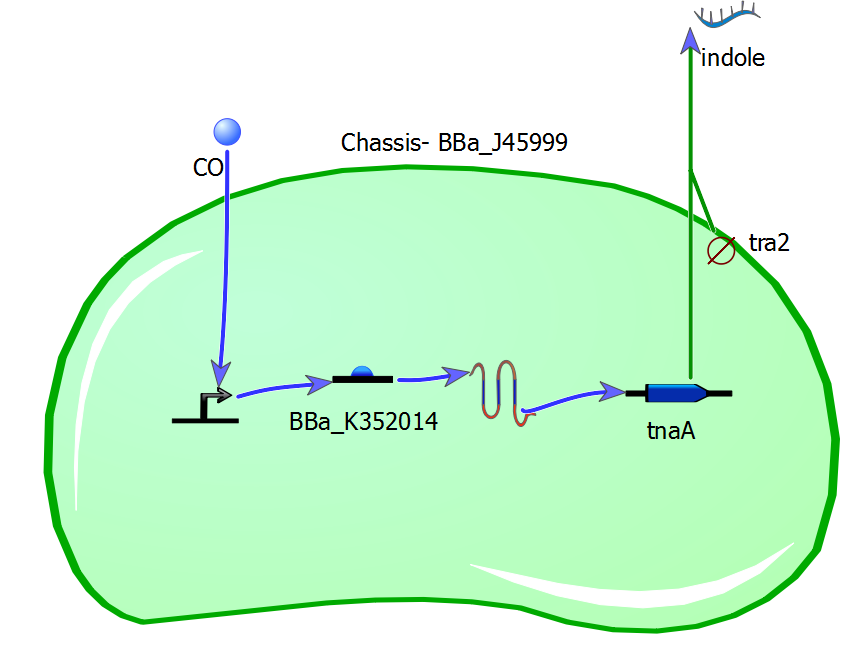
Parts We are Considering
Chasis: [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_J45999 BBa_J45999]
CooA: [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K352014 BBa_K352014] (CooA coupled with placI and RBS)
tnaA: (for indole production)
- issue: we don't know if we can find a tnaA gene
three genetic circuits we are considering: one with GFP one with indole one with banana.
FUNdraising
Saturday, December 2011
The first fundraiser our team organized was a bake sale at a local sports complex. The Tyngsborough Sports Center was generous enough to allow us to set up a table one Saturday in December and we sold an assortment of homemade baked goods and ornaments. Since it was close to Christmas, our team had a meeting dedicated to making ornaments out of pipe cleaners which we dipped in (what was it again?) to crystallize them. The day of the fundraising, team members came in for their designated shifts throughout the day and we all brought different types of baked goods to sell as well. Making the ornaments was a fun team activity and we also had fun spending time together at our different shifts. Best of all, we made $300 for our team!
Friday, February 2012
The second fundraiser our team set up was to run the concession stand at one of the girl's varsity basketball game. Our principal kindly allowed us to sell pizza, candy, drinks, and once again, homemade baked goods, for the concessions at our High School's girl's varsity basketball game. We set up a table outside the gym and during the game, sold all of the food to make a profit of $250. Overall Tyngsborough High School had a successful night because our iGEM team was able to raise even more money, and the girls team won the game!
Saturday, May 2012
Synthetic Biology Outreach
Results/Conclusions
What did you achieve over the course of your semester?
SAFETY
What safety precautions did your team take? Did you take a safety training course? Were you supervised at all times in the lab?
Each member of the Tyngsborough Igem Tiger Squad has learned and currently follows the Flynn's scientific safety contract. Each new year, we take a scientific safety refresher to brush up on our safety procedures. We are all supervised in our labs by our instructors Mrs. Boughan and Mrs. Ravigala.
Here is a link to youtube to watch a funny safety video on what NOT to do in a lab setting.
[http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GOQAq4Nl4og Click here for video] All credit goes to the producer of the video Zach Lipovsky
[http://bio.pgp.jhu.edu/~genbiolab/safety.mov Here is a video showing what to do when in a lab!]
[http://rushartsbiology.wikispaces.com/file/view/Lab%20Equip%20Lists.pdf Click here for a Lab equipment List]
Attributions
Who worked on what?
Human Practices
Currently, the common CO detectors on the market are only sound-based. However, as people age, their senses aren't quite what they used to be, and our cell could help save even more lives with another sensory warning of the hidden danger. Also, many work places, such as construction sites, are extremely loud, easily loud enough to drown out the little beeping of a sensor, however, a disgusting and identifiable smell permeating through the compound could again save even more lives. Coupled with the common household detector, our cell could greatly reduce the number of CO deaths per year.
Fun Facts!
Didja Know?
"Males are 2.3 times more likely to die from CO poisoning than females." (utahpersonalinjurylawfirm)
http://www.epa.gov/otaq/invntory/overview/images/charts/co_by_source_onroad.gif
http://www.surveymonkey.com/s/C5XN8HP
References
1. "Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Statistics." Christensen Law Firm. 03 Sept. 2010. Web. 1 Mar. 2012. [<http://www.utahpersonalinjurylawfirm.com/2010/09/carbon-monoxide-poisoning-statistics/>].
2. November. 2011. Web. 1 Mar. 2012. http://www.ncsl.org/issues-research/env-res/carbon-monoxide-detectors-state-statutes.aspx
3. Fox, Jeffrey D., Robert L. Kerby, Gary P. Roberts, and Paul W. Ludden. "Characterization of the CO-Induced, CO-Tolerant Hydrogenase from Rhodospirillum Rubrum and the Gene Encoding the Large Subunit of the Enzyme." Journal of Bacteriology (1996): 1515-524. American Society for Microbiology, Mar. 1996. Web. 12 Jan. 2012.
4. Mar. 2012. http://bestanimations.com/animals/mammals/cats/tigers/tigerroaringanimation-18.gif/
5. Wood, W. A., I. C. Gunsalus, and W. W. Umbreit. Function of Pyridoxal Phosphate: Resolution and Purification of the Tryptophanase Enzyme of Escherichia Coli. Publication. Ithaca: Labaratory of Bacteriology, College of Agriculture, Cornell University, 1947. Web. 22 Mar. 2012. <http://www.jbc.org/content/170/1/313.full.pdf>.
 "
"


