Team:Dalton School NY/Notebook
From 2012hs.igem.org
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | In progress... | |
| - | PCR of promoters and fluorescent protein coding sequences | + | ==Testing of DNA prepared by several methods== |
| + | |||
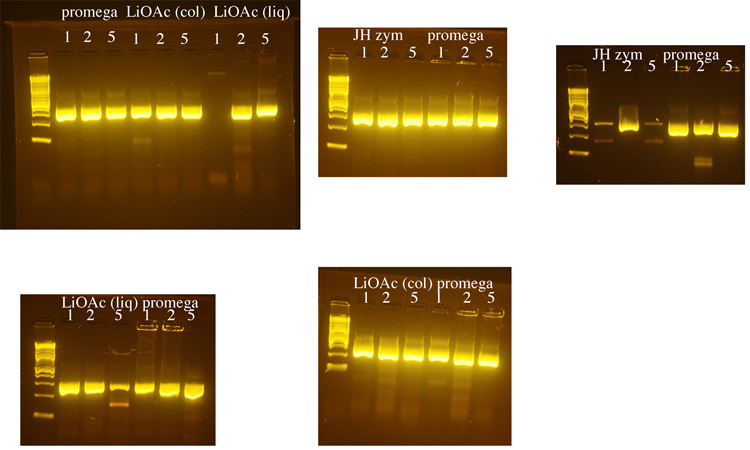
| + | Yeast genomic DNA is commonly prepared using a phenol/chloroform based method. Because both phenol and chloroform are toxic chemicals, we tested several methods for preparing yeast genomic DNA that do not use these chemicals. We compared a method that uses LiOAc to disrupt the yeast cell wall (BioTechniques 50:325-328, 2011) to methods that use the enzyme zymolyase to disrupt the cell wall (a Promega kit or a protocol from Jim Haber’s lab, “JH zym”). The Haber lab protocol produced the greatest yield of genomic DNA, but DNA made using the Promega kit was used in subsequent PCRs because it seemed to produce the most consistent results. 1µl, 2µl, or 5µl of genomic DNA was used in each PCR reaction with LIF1 promoter primers. Following these initial tests, 1µl of yeast genomic DNA was used for subsequent PCRs. The LiOAc method was the shortest and least expensive and we may switch to this method when future DNA preps are needed. | ||
| + | [[Image:Dalton_Fig7.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
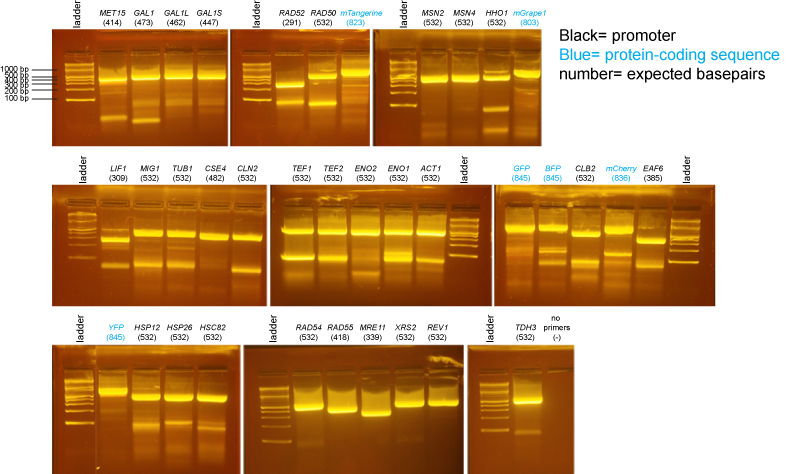
| + | ==PCR of promoters and fluorescent protein coding sequences== | ||
[[Image:Dalton_Fig6.jpg]] | [[Image:Dalton_Fig6.jpg]] | ||
Return to our [https://2012hs.igem.org/Team:Dalton_School_NY main page]. | Return to our [https://2012hs.igem.org/Team:Dalton_School_NY main page]. | ||
Revision as of 20:39, 29 May 2012
In progress...
Testing of DNA prepared by several methods
Yeast genomic DNA is commonly prepared using a phenol/chloroform based method. Because both phenol and chloroform are toxic chemicals, we tested several methods for preparing yeast genomic DNA that do not use these chemicals. We compared a method that uses LiOAc to disrupt the yeast cell wall (BioTechniques 50:325-328, 2011) to methods that use the enzyme zymolyase to disrupt the cell wall (a Promega kit or a protocol from Jim Haber’s lab, “JH zym”). The Haber lab protocol produced the greatest yield of genomic DNA, but DNA made using the Promega kit was used in subsequent PCRs because it seemed to produce the most consistent results. 1µl, 2µl, or 5µl of genomic DNA was used in each PCR reaction with LIF1 promoter primers. Following these initial tests, 1µl of yeast genomic DNA was used for subsequent PCRs. The LiOAc method was the shortest and least expensive and we may switch to this method when future DNA preps are needed.
PCR of promoters and fluorescent protein coding sequences
Return to our main page.
 "
"